Biomass Power Generation
Biomass power generation uses biological materials (called biomass) such as waste or residue from logging or
agriculture as fuel to generate electricity.
RENOVA uses wood chips from domestic unused timber or forest residue, as well as wood pellets and palm kernel
shells (PKS) from overseas as biomass fuel.
-
Characteristic of Biomass Power Generation
Through photosynthesis, chloroplasts of plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the air and utilize it to grow the plant’s body. Consequently, power generation fueled by biomass is regarded as carbon neutral as it only releases carbon dioxide that was absorbed during the plant’s growth. Using biomass fuels as an alternative to fossil fuels enables power generation to reduce CO2 emissions globally and consequently to contribute to the prevention of global warming. Utilizing domestic biomass resources also contributes to revitalizing the domestic economy through the creation of new business fields and the provision of employment opportunities to the local community. These opportunities include not only power plant operation jobs but also harvesting and collecting biomass from forests and transporting biomass to power stations.
-
Mechanism of Biomass Power Generation
Biomass Power Generation that RENOVA develops and operates is categorized as thermal power generation. In other words, by burning biomass fuel, it produces high-temperature and high-pressurized steam that rotates turbines to generate electricity. Consequently, biomass power generation can serve as a baseload electricity source, as it is controllable and is not affected by weather and/or atmospheric conditions.
-
Our Approach to Biomass Fuels
Responsible fuel procurement
At our biomass power plants, we procure fuels that comply with government guidelines and ensure the legality, sustainability, and traceability of fuels through third-party certification and other means.
In addition, we have established our own “Sustainable Procurement Policy for Biomass Fuels” and conduct surveys and interviews with major suppliers to confirm that this policy is being met.Contributing to CO2 Reduction
The greenhouse gases emitted from the entire process of biomass fuel from the procurement of raw materials to combustion at the power plant (including manufacturing and transportation) are referred to as “Life-cycle CO2”. Our biomass power plants reduce Life- cycle CO2 emissions by more than 80% compared to conventional thermal power plants. This significantly contributes to mitigating global warming.
- *1Life-cycle CO₂ of thermal power generation assuming the energy mix in 2030
(Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Business Planning Guidelines) - *2As an average value of our power plants
- *3Power generation using biomass resources, which grow by absorbing CO₂ through photosynthesis, is considered to be CO₂ emission-free under the Kyoto Protocol.
(Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, Nattoku! Renewable Energy)
- *1Life-cycle CO₂ of thermal power generation assuming the energy mix in 2030
Biomass Power Plants
-
 Akita BiomassAkita-shi, Akita Prefecture, Japan
Akita BiomassAkita-shi, Akita Prefecture, Japan- July 2016
In Operation -
 Ishinomaki Hibarino BiomassIshinomaki-shi, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan
Ishinomaki Hibarino BiomassIshinomaki-shi, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan- March 2024
In Operation -
 Sendai Gamo BiomassSendai-shi, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan
Sendai Gamo BiomassSendai-shi, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan- November 2023
In Operation -
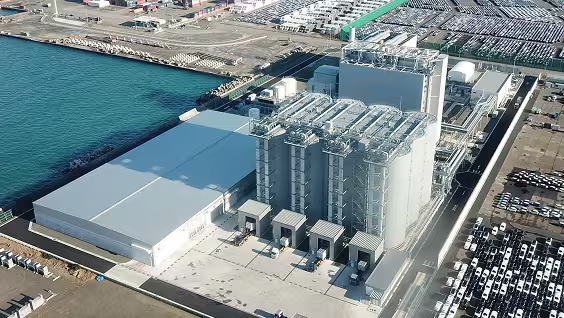 Omaezakikou BiomassOmaezaki-shi and Makinohara-shi, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan
Omaezakikou BiomassOmaezaki-shi and Makinohara-shi, Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan- January 2025
In Operation -
 Tokushima Tsuda BiomassTokushima-shi, Tokushima Prefecture, Japan
Tokushima Tsuda BiomassTokushima-shi, Tokushima Prefecture, Japan- December 2023
In Operation -
 Kanda BiomassKanda-machi, Miyako-gun, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan
Kanda BiomassKanda-machi, Miyako-gun, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan- June 2021
In Operation -
 Karatsu BiomassKaratsu-shi, Saga Prefecture, Japan
Karatsu BiomassKaratsu-shi, Saga Prefecture, Japan- september 2025
In Operation
